Topics
1.Define Web Services in java

1.Define Web Services in java
Web Services tutorial is designed for beginners and professionals providing basic and advanced concepts of web services such as protocols, SOAP, RESTful, java web service implementation, JAX-WS and JAX-RS tutorials and examples.
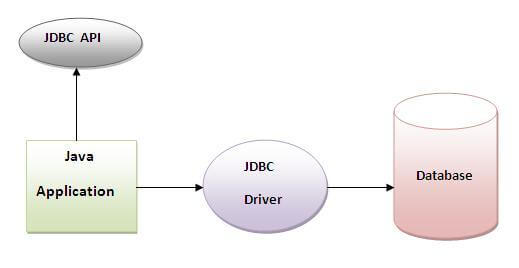
Web service is a technology to communicate one programming language with another. For example, java programming language can interact with PHP and .Net by using web services. In other words, web service provides a way to achieve interope
Web Services Examples
In this tutorial, we will see a lot of web services examples like JAX-WS example by RPC style, JAX-WS example by document style, JAX-RS example by Jersey and JAX-RS example by RESTeasy implementation.