Inheritance is one of the feature of Object-Oriented Programming (OOPs). Inheritance allows a class to use the properties and methods of another class. In other words, the derived class inherits the states and behaviors from the base class. The derived class is also called subclass and the base class is also known as super-class. The derived class can add its own additional variables and methods. These additional variable and methods differentiates the derived class from the base class.
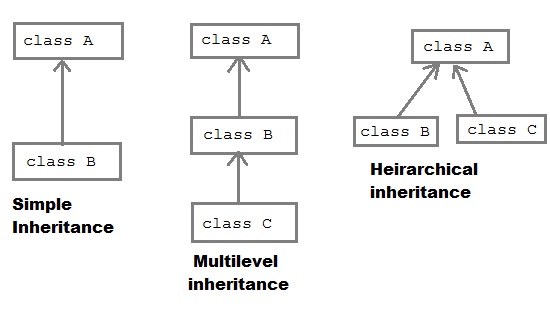
Inheritance is a compile-time mechanism. A super-class can have any number of subclasses. But a subclass can have only one superclass. This is because Java does not support multiple inheritance.
The superclass and subclass have “is-a” relationship between them. Let’s have a look at the example below.
Inheritance Example
Let’s consider a superclass
Vehicle. Different vehicles have different features and properties however there few of them are common to all. Speed, color, fuel used, size are few which are common to all. Hence we can create a class ‘Vehicle’ with states and actions that are common to all vehicles. The subclass of this superclass can be any type of vehicle. Example: Class Car A has all the features of a vehicle. But it has its own attributes which makes it different from other subclasses. By using inheritance we need not rewrite the code that we’ve already used with the Vehicle. The subclass can also be extended. We can make a class ‘Sports Car’ which extends ‘Car’. It inherits the features of both ‘Vehicle’ and ‘Car’.
The keyword used for inheritance is extends. Syntax:
public class ChildClass extends BaseClass { // derived class methods extend and possibly override }
Here is the complete example:
// A class to display the attributes of the vehicle class Vehicle { String color; int speed; int size; void attributes() { System.out.println("Color : " + color); System.out.println("Speed : " + speed); System.out.println("Size : " + size); } } // A subclass which extends for vehicle class Car extends Vehicle { int CC; int gears; void attributescar() { // The subclass refers to the members of the superclass System.out.println("Color of Car : " + color); System.out.println("Speed of Car : " + speed); System.out.println("Size of Car : " + size); System.out.println("CC of Car : " + CC); System.out.println("No of gears of Car : " + gears); } } public class Test { public static void main(String args[]) { Car b1 = new Car(); b1.color = "Blue"; b1.speed = 200 ; b1.size = 22; b1.CC = 1000; b1.gears = 5; b1.attributescar(); } }
The output is
Color of Car : Blue Speed of Car : 200 Size of Car : 22 CC of Car : 1000 No of gears of Car : 5
No comments:
Post a Comment